Android: Testing
2021-03-04
About
An overview about Testing in Android. The following topics are covered.
- Basic Testing
- Testing Repository, ViewModel, Fragments
- Testing Navigation, Coroutines, Room, Databinding
Introduction
When you create a new android project you get a default testing setup.
If you look at your project you will see three so called source sets.
androidTest and test contains your tests
$ tree -d -L 2 app/src/
app/src/
├── androidTest
│ └── java
├── main
│ ├── java
│ └── res
└── test
└── java
The default dependencies defined in gradle are junit and espresso library
You may noticed that the test folder represents the junit library. Where you test your code, classes in main folder.
For the android test dependency espresso library is used.
As a quick refresher. How to run a test in android studio: open your ExampleUnitTest class > mark the method annotated with @Test > right click > Run ...
Android Test
The android test folder contains test which run on the android system. Not like the junit test which run on the local machine JVM (default java behaviour). The android test are also called instrumented test whereas junit test are called local test.
To run an android test works same way as junit. After running an android test you should see something like androidx.test.runner.AndroidJUnitRunner. Which is an indication of running an android test.
TDD
We have seen that android gives us the default (plus android test) environment to code in Test Driven Development methodology.
TDD: write test first, run test first and then implement the feature
The testing code is also a kind of a documentation what your code does.
Good practices
- Use good naming. Example:
subjectUnderTest_actionOrInput_resultState. - Structure your test code using Given / When / Then.
@Test
fun getDeveloper_expert_returnsExpert() {
// GIVEN
val devs = listOf<Developers>(Developer(experience=10), Developer(experience=15), Developer(experience=30))
// WHEN
val result = getNumberOfSeniorDevelopers(devs)
// THEN
assertEquals(3, result)
}
- Use an assertion framework. For example hamcrest framework. For hamcrest you need to add the dependency in your build file. Example usage (differs from junit assertion)
// `is` so called _matcher_
assertThat(result, `is`(3))
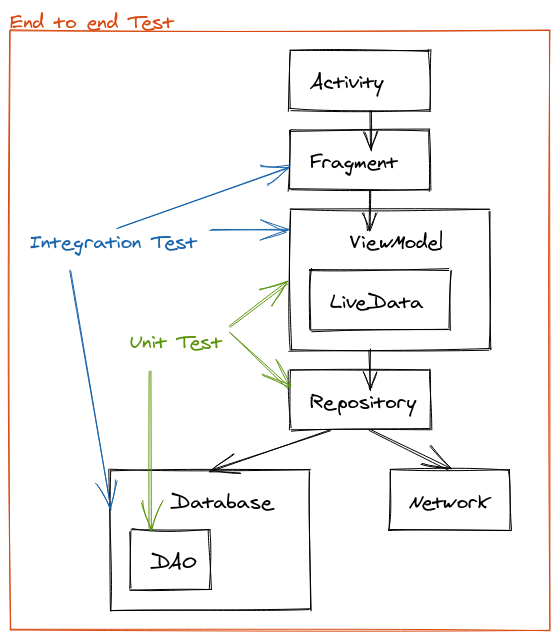
Test scope aka. Testing Pyramid
On automated testing generally three test scopes are used:
- Unit tests: scope is class, function
- Integration tests: a combined test. Test how components work together. Ensure that a features works as expected.
- End to end test: test the combination of features. In android context this is almost instrumented testing.
Btw. you will also find other testing pyramid specification. But this three layer definition should enough for most purposes.
Recommendation for coverage is:
- Unit Tests: 70%
- Integration Tests: 20%
- E2E Tests: 10%
But my thoughts are the main impact does the end to end tests.
A big issue is also if you have a large function or other components with lot of dependencies. It's difficult to test. In that case you can do an end to end test. But creating unit test could be in that case difficult.
That's why you should break down your application logic into isolated components. With a well defined (best practice) application architecture you can divide your code in a defined way.
What to do if you havent a well structured code or legacy code?
- (only) Refactor code where you have tests
- write test where its easily possible
- you can always write end to end tests
- for new features use an architecture
Unit Testing
Run test in JVM instead of Android ecosystem.
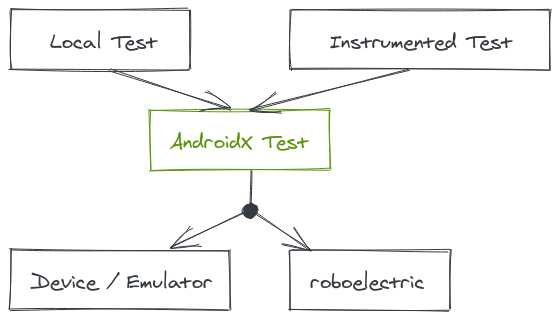
We sad that unit testing (with JUnit) is a local test and faster then an instrumented test. In some cases we need an application context. In order to get that component Android provides AndroidX Test libraries.
- To use it you need to add the following dependencies:
- AndroidX Test core
- roboelectric: creates a simulated android environment for local tests
- AndroidX Test Kotlin: needed for the AndroidJUnit Runner
testImplementation "androidx.test:core-ktx:$androidXTestCoreVersion"
testImplementation "org.robolectric:robolectric:$robolectricVersion"
testImplementation "androidx.test.ext:junit-ktx:$androidXTestExtKotlinRunnerVersion"
- Afterwards in your JUnit test class you also need to annotate you class.
You can then use e.g. a
ViewModelwhich expects an application context.
@RunWith(AndroidJUnit4::class)
class DeveloperTest {
@Test
fun addNewDeveloper_setsNewDeveloperEvent {
val viewModel = DeveloperViewModel(ApplicationProvider.getApplicationContext())
}
}
With AndroidX Test libraries we can reuse code in both environments (local and instrumented). To conclude AndroidX Test provides a unified API.
Test Doubles
Like stunt doubles we can create test doubles to replace a production object for testing purposes. There are various kind of doubles: Dummy, Fake, Mock, Stub, Spy
Links
- https://github.com/udacity/android-testing.git
- https://developer.android.com/training/testing/fundamentals
- https://developer.android.com/training/testing/set-up-project
- https://martinfowler.com/bliki/TestDouble.html